Your business.
Your vision.
Our expertise.
The result? Satisfied customers and growing sales.
They already feel
the impact of using
a CRM system
Choose your path
to CRM implementation
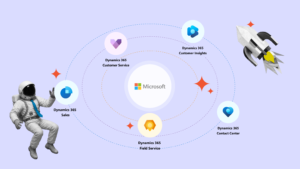
Ecosystem
- Dynamics 365 Sales Sales management
- Dynamics 365 Field Service Field service management
- Dynamics 365 Customer Service Process automation for service and support
- Dynamics 365 Customer Insights Data unification and enrichment, personalized offers and communication
- Dynamics 365 Contact Center Contact center operations management
Platform
- SMART Sales Automate the entire B2B sales cycle — from the first lead to a signed deal.
- SMART Marketing Manage omnichannel marketing communications with your customers.
- SMART Customer Care Register and process customer service requests.
- SMART Order Management Register and process orders in B2C sales.
development
- If your business processes are unique and customizing ready - made systems is too complex or costly, we can build automation from scratch.
- We create lightweight solutions and applications that cover all CRM-related tasks.
Any CRM solution can be enhanced with AI
Forecast deal closures, personalize offers, and automate responses effortlessly — AI is already working for you!
Expand your system with SMART connectors


Which scenario
is right for you?
CRM That Works for Your Business
CRM That Works for Your Business
CRM That Works for Your Business
CRM That Works for Your Business
CRM That Works for Your Business
CRM That Works for Your Business
Frequently Asked Questions
- You are losing potential leads.
- Your communication is inconsistent — several managers reach out to the same customer.
- Your internal processes are slow.
- You can’t keep up with new customer demand and a rapidly growing client base.
- You make decisions intuitively because you don’t have insights into which marketing campaigns perform best.
- You manage data, teams, and customers manually.
- A 360-degree customer view
- Easy integration with other services
- Built-in analytics and AI
- Omnichannel communication with customers and prospects
- Tools for task and team management
- Mobile access and cloud availability
- Flexibility and scalability
- Marketing automation
- B2C sales
- B2B sales
- Service operations
- Installing the solution and deploying the required Microsoft base infrastructure.
- Deploying and testing the out-of-the-box solution.
- Preparing templates for initial data import.
- Training key users on system functionality, as well as training analysts and administrators for future self-configuration.
- Go-Live.
Why choose
SMART business?
We automate business processes for companies worldwide. We operate through offices in Ukraine, Poland, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Spain — with local experts who speak the clients’ language and understand the specifics of regional markets.
The SMART business team regularly completes Microsoft training and certifications, so the specialists working on your project apply the latest technologies and up-to-date expertise.
We adhere to the principle of transparency: we recommend only those tools and licenses that directly match your needs.
Our solutions are built on international best practices, so you receive not just software — but also guidance on how to structure your business processes for real impact.