What Is Omnichannel in Business and How Does It Streamline Customer Interaction?

In the world of Internet Customer Service, it’s important to remember your competitor is only one mouse click away.
Today’s business reality is one where the customer journey is not linear but rather resembles a metro map with numerous stations, transfers, and spontaneous stops. Along this journey, the brand must accompany the customer wherever they turn — whether it’s a messenger, social media, a website, or a physical store. The modern customer journey is a complex system of turns, repeated contacts, and unexpected interaction points. Yet, customers expect a seamless, convenient, and personalized experience with the brand, regardless of where their journey begins. This is why omnichannel has become a strategic necessity in business.
What Is Omnichannel?
Omnichannel means seamless, unified communication with the customer that preserves the essence of the dialogue regardless of where it takes place. By consolidating all communication channels into a single system, a company can personalize its interaction with the customer by enriching their profile. Every point of contact between the consumer and the company collects information about the customer, and all other channels have access to this data. This way, omnichannel enables businesses to see the full picture and respond quickly, consistently, and personally.
Omnichannel usually integrates data from the following communication channels:
- Company website
- Mobile app
- E-mail campaigns
- Messengers (Viber, Telegram, WhatsApp, etc.)
- Contact center (telephony)
- Online advertising
- Offline sales points
- Social media
- Service support systems (ticketing, help desk)
- Chatbots and AI assistants
What Is Multichannel?
Omnichannel begins with multichannel because first, a customer must be able to contact the company through various platforms — depending on which is most convenient for them. Multichannel means having multiple communication channels (e-mail, phone, social media, messengers, offline locations) that customers can use to get information or support. However, these channels usually operate independently and are not synchronized: interaction histories don’t transfer between them, and each new contact starts “from scratch”. This is the first step toward more convenient service, but without data integration and continuous dialogue, such an approach often fragments the customer journey.
What Is the Difference Between Omnichannel and Multichannel?
The difference between multichannel and omnichannel lies not just in the number of channels but in how these channels interact with each other. In multichannel, a customer can reach the company via different platforms — but each functions separately, without sharing data. For example, an e-mail inquiry won’t be linked to a message sent via a messenger, so the customer must repeat information about their order each time. In contrast, omnichannel unites all these channels into a single system: no matter which channel the interaction starts or continues on, customer data, interaction history, preferences, and statuses are stored and synchronized.
Omnichannel in Practice — in Sales and Customer Service
According to data from Digital Commerce 360, companies with effective omnichannel interaction show an annual revenue growth of 9.5%, while businesses with weaker strategies achieve only 3.4%. How exactly does this work in the context of company–customer communication?
In sales, omnichannel means that a customer, for example, starts their selection on the website, clarifies details on Instagram, makes a purchase via a mobile app, and picks up the product in a physical store — with each stage conveniently integrated and logically complementing the previous one. All customer actions are synchronized in a single system (usually a CRM system) that combines analytics tools, an e-commerce platform, and all communication channels. Thanks to this, the brand not only records every contact but also understands the context — which products were viewed, what questions arose, and which payment method is preferred. This enables personalized offers and process optimization: ensuring product availability in a specific store, reducing service time, minimizing returns, and more. Omnichannel sales build a unified interaction logic that guarantees comfort for the customer and higher conversion and repeat purchases for the business.
In customer service, omnichannel means care without disruptions or unnecessary repeats. For example, the operator already sees the issue the customer raised yesterday via chat, and the service team continues the conversation over the phone from where it left off — without needing the customer to explain everything again. This is possible thanks to the integration of communication channels (chatbots, e-mail, telephony, messengers) with the CRM system, which stores the full interaction history in real time. Every employee sees the status of the request, colleagues’ notes, attached files or complaints, as well as the customer’s segment and profile. This not only saves time and reduces frustration but also improves overall customer satisfaction (CSAT) and reduces repeat inquiries.
Advantages of Omnichannel Customer Service:
- For the business: Omnichannel guarantees coordinated channel operation, reduces response time, lowers service costs, and forms a comprehensive picture of customer needs. Data from different sources no longer exist separately — they are unified into a single system that enables more accurate decisions and helps build long-term relationships.
- For the customer: Omnichannel means, above all, convenience and consistency — the ability to receive the same quality of service regardless of the channel — online or offline. Every interaction is accounted for, interaction history is preserved, and personalized solutions are offered from the very first minutes. This approach creates a sense of trust and professionalism, which directly influences brand loyalty.
What is Omnichannel Marketing and How to Develop an Effective Omnichannel Marketing Strategy
In marketing, omnichannel means seamless communication where a customer sees a banner on the website, receives a personalized offer in a messenger, and then a reminder by e-mail with a relevant product in the cart. Thanks to the integration of marketing channels with CRM systems, analytics, and automated scenarios, businesses can send accurate and timely messages in a convenient format — considering the customer’s behavior, preferences, and previous interactions. This not only improves campaign effectiveness but also retains audience attention without intrusiveness, preserving trust in the brand.
Building a quality omnichannel marketing strategy starts with creating a portrait of the omnichannel customer. After all, the customer is at the center of this communication — they set the rules, choose communication channels, and points of interaction with the company. These choices and behavior patterns should be taken into account when forming the customer profile.
Building a Personalized Customer Profile: What to Consider
The average omnichannel customer typically:
- Prefers BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store) — orders a product on the website and picks it up in a physical store. According to statistics from Fireworks, 50% of shoppers prefer BOPIS, and 67% of them make additional purchases while collecting their order in-store.
- Frequently orders products online with home delivery.
- Tracks and compares prices on websites or in apps.
- Installs store or brand apps to make ordering products or services more convenient and to receive updates on discounts and promotions.
- Subscribes to e-mail or messenger newsletters from the company to monitor deals and new arrivals.
- Actively leaves feedback and suggestions via chatbots, social media, or phone support.
Using these common patterns as a foundation, you can start building more personalized customer profiles — for instance, a Customer Journey Map.
CJM for the Omnichannel Customer and How to Build One
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) is an analytical tool that helps a business visualize the customer’s interaction with the company at every stage of their journey — from the first contact to purchase and post-sale service. This map clearly outlines which touchpoints the customer encounters, what obstacles they face (e.g., a hard-to-find checkout button or a long hotline queue), what emotions accompany their decisions, and at which stages the company loses effectiveness.
The more detailed the map, the more precisely you can identify critical blockers: non-functional CTAs, complex registration forms, overwhelmed support teams, or inconsistent cross-channel communication. Focusing on real customer segments allows for the setup of personalized scenarios, automation of interactions, and tailoring of content to specific user needs.
Calculating CLV — the Next Step in the Strategy
To build an effective omnichannel marketing strategy after developing a customer profile, the next step is to calculate their CLV (Customer Lifetime Value). This metric allows a business to assess the actual long-term value of a customer to the company. With CLV, a business can segment its customer base, tailor communication, prioritize support, and make informed decisions about where to invest time and budget — and where to optimize spending.
CLV is the total revenue a customer generates over the entire period of interaction with the brand — for example, over a year or the average customer lifecycle.
Let’s say a buyer spends ₴2,000 every two months. Their annual value (CLV) would be calculated as 6 × 2,000 = ₴12,000. However, if supporting this customer requires two hours of service each month and one hour of a specialist’s time costs ₴500, then the annual service cost equals 12 × 2 × 500 = ₴12,000. As a result, the company earns no profit from this customer. Identifying such cases in time is crucial to optimize resources and focus on customers with higher potential value.
By creating an omnichannel customer profile and calculating their CLV, a company is ready to begin building a data-driven omnichannel marketing strategy.
How to Work with an Omnichannel Customer: Tips and Insights

The growing number of communication channels opens up new opportunities for engaging with customers — but it also makes managing those interactions more complex. Without a unified strategy, communication quickly turns into chaos, where marketing becomes ineffective and customer trust is lost. While every company must choose its own path to customer engagement, here are a few universal recommendations to help make the process as effective as possible:
- Identify key touchpoints
You don’t need to be everywhere — you need to be where your customer is. Analyze the platforms and channels your audience actually uses, and focus on those that ensure stable, measurable engagement: website, messengers, e-mail, social media, physical locations, app, and so on.
Tip: Keep your number of touchpoints optimal. Respect both your budget limits and your customer’s privacy — too many newsletters, promotions, or surveys may backfire and damage the experience. - Ensure technical integration between channels
Your CRM, marketing platforms, analytics, chatbots, contact center, and e-commerce modules should all be synchronized. All customer data — orders, interaction history, campaign responses — should be accessible in a single view. - Build personalized engagement flows
Use customer data (behavior, purchase history, content interactions) to develop automated communication flows: welcome sequences, abandoned cart reminders, personalized follow-ups, dynamic discounts for loyal customers. Personalization should always make sense in the context of that specific customer. - Implement cross-channel analytics
Track not only the effectiveness of each channel individually but also how customers move between them. Monitor KPIs such as conversion rate, time to purchase, cost per contact, open and click-through rates. This will help you pinpoint bottlenecks and growth opportunities — for example, when customers start in Instagram but don’t complete purchases on your site. - Maintain brand consistency
Your brand voice, visual style, and value proposition should be aligned across all platforms. A customer shouldn’t feel like they’re dealing with different companies on Facebook, via the call center, or at a pickup point. - Establish feedback loops and run tests
Make sure every omnichannel campaign includes a way to gather feedback. What are your customers saying? Where is communication breaking down? A/B testing messages, formats, and channels will help you continuously improve customer experience. - Regularly review your strategy
Channels evolve — and so does customer behavior. Keep your customer journey maps, segments, flows, and campaign logic up to date. Your strategy shouldn’t be static — it should evolve alongside your audience. - Deploy AI assistants and chatbots
Automate basic inquiries and repetitive tasks using chatbots and AI-powered assistants. They can instantly handle standard questions, help place orders, or offer recommendations based on purchase history or user behavior. Modern AI tools can understand context and even adapt to changes in customer behavior, delivering a fast, effective, and personalized experience — 24/7.
How to Choose the Right Tools to Automate Your Omnichannel Marketing Strategy: What to Look For and What the Market Offers
Choosing the right tools to automate your omnichannel marketing strategy isn’t just about convenience — it’s a critical step in building strong, lasting relationships with your customers. So, what should you consider when selecting a platform?
- Integration with existing systems: The solution should integrate seamlessly with your current platforms (CRM, CDP, e-commerce, analytics) to ensure consistent data flow and efficient information exchange between systems.
- Flexible communication channels: Your platform must support a variety of communication channels — e-mail, social media, messengers, phone, and website chat. All channels should be consolidated into a single system to enable continuous dialogue with the customer.
- Communication automation: The tool should support setting up automated notifications, messages, and communication flows for every stage of the customer journey — such as order confirmations, abandoned cart reminders, and more.
- Personalization capabilities: Look for a solution that enables you to deliver personalized offers based on customer data, behavior, and purchase history. This directly impacts the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
- Data analysis and reporting: The platform should provide tools for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data across each customer interaction channel — allowing you to track performance metrics and adjust your strategy in real time.
- Customer profile management: You should be able to create and maintain a unified profile for each customer by consolidating data from all touchpoints.
- Scalability and flexibility: Your tool should scale as your business grows and adapt to new channels or changing needs without requiring major restructuring.
- User-friendliness: An intuitive, easy-to-use interface is essential to ensure your team can quickly adapt to new workflows and settings.
- Data security: Protecting customer data is a top priority. The platform you choose must comply with security standards and ensure the confidentiality of customer information.
- Ongoing support and updates: The tool should come with reliable technical support and regular updates to keep pace with market demands and emerging technologies.
SMART business offers a suite of solutions that meet all these requirements. Let’s explore how the functionality of these tools can help automate your marketing processes and enhance your customer engagement strategy.
SMART CRM, Microsoft Dynamics 365, SMART EasyBot, and SMART Chat: How These Tools Optimize Your Omnichannel Strategy
SMART CRM is a comprehensive CRM platform designed to automate sales, marketing, and customer service processes by consolidating all essential trade data in a single digital environment.
The CRM system includes four core modules, which can be implemented individually or together: SMART Sales, SMART Customer Care, SMART Order Management and SMART Marketing.
The platform also offers seamless integration with a variety of key connectors, such as SMART Connector for Telephony, SMART Connector for GMS, SMART Connector for Ringostat, and others.
Implementing SMART CRM or its individual modules helps businesses automate customer communication at every stage of the journey, consolidate all communication channels into a unified workflow, efficiently analyze customer behavior, and reduce the manual workload for marketing and service teams.
Two additional CRM modules — SMART Chat and SMART EasyBot — are particularly useful for building an effective omnichannel marketing strategy:
- SMART Chat enables your business to consolidate all messaging platforms (Telegram, WhatsApp, Viber, Instagram, etc.) into one clear communication stream, while automatically syncing customer data into Dynamics 365 or SMART CRM. This unlocks additional opportunities for personalized engagement.
- SMART EasyBot is a chatbot that automates customer communication on Viber and Telegram. It supports sending personalized messages, building interactive menus, handling inbound requests, launching segmented campaigns, and managing everything directly from the CRM system. The bot integrates with customer profiles, supports user registration, and enables self-service flows.
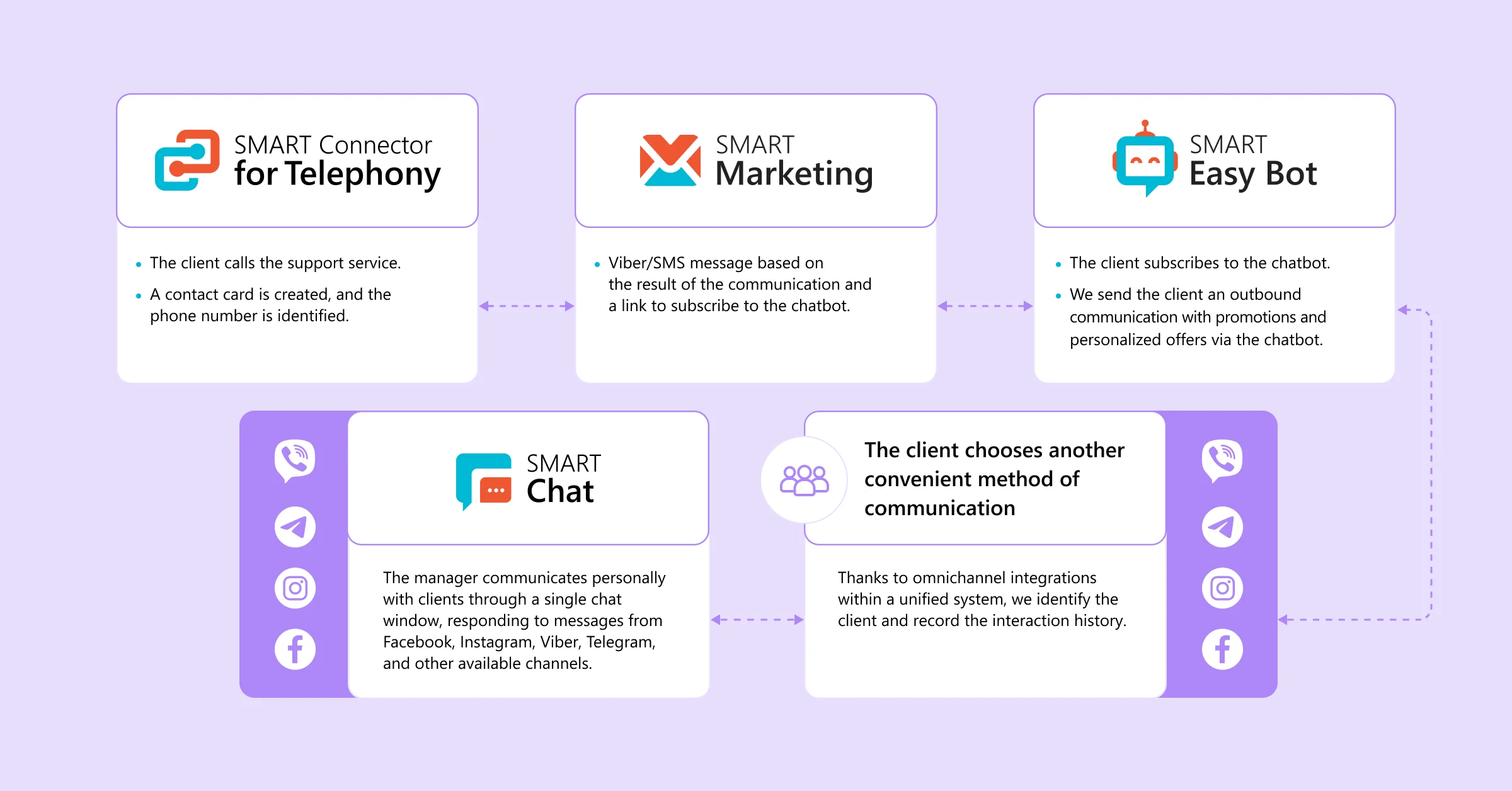
By selecting the tools most relevant to your business and integrating them into a single ecosystem, you can build a seamless chain of interactions that keeps the customer engaged throughout the sales funnel. For example:
- A customer calls the company. A customer record is automatically created via SMART Connector for Telephony, based on their phone number.
- Using SMART Marketing, an SMS or messenger message is sent with a summary of the conversation and a link to a chatbot.
- The customer subscribes to SMART EasyBot and begins receiving personalized offers through the bot.
- The customer chooses their preferred channel of communication — for instance, selecting from five available messengers.
- A manager continues the personalized conversation using SMART Chat, communicating with customers across multiple messengers — all from one convenient interface.
Real-World Use Cases: Managing Omnichannel Interactions with SMART business Solutions
Ultimately, the best way to showcase any solution’s capabilities is through real-world results. Here are two examples of how SMART business helps optimize omnichannel marketing:
Brocard, the largest perfume retail chain in Ukraine, implemented Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights along with SMART Connector for GMS to automate Viber/SMS campaigns, analyze customer behavior, and send trigger-based messages (e.g., birthday reminders or abandoned cart follow-ups). This allowed the company to move beyond one-time promotions and offer personalized customer experience to over 1.8 million consumers.
LEOLAND, a sports and entertainment complex in Lviv, integrated Dynamics 365 Sales with SMART Connector for Binotel, SMART Chat, Easy Bot, eSputnik, and GMS to automate e-mail/SMS/Viber campaigns, telephony, chatbots, and Power BI analytics — all within a single CRM ecosystem. As a result, LEOLAND visitors enjoy not only the entertainment experience but also flawless service and communication.
If you’re also looking for solutions to automate your omnichannel strategy — request a demo, and SMART business experts will help you choose the tools that fit your goals: