Customer Journey Map: Streamlining Business Processes and Removing Barriers Along the User Path

The modern era of overproduction is increasingly being called the age of meaning-makers, where businesses offer consumers not just products, but personalized value.
According to a Benchmark study, 87% of fast-growing companies actively apply the “value creation” approach. Their experience shows a clear link between the effort a business invests in building a strong emotional connection with customers and its sales performance.
Businesses understand well: “How to strike the right chord with the customer and secure a lasting place in their heart” is not some magical ritual – it’s a matter of collecting and processing data. And for that, effective tools are essential.
CRM is the most popular among them, but not the only one. Another must-have is the Customer Journey Map (CJM).
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
It is a method of visualizing how customers interact with a company at different stages of their journey. It helps to understand their needs and emotions at every touchpoint with the brand.
That’s why experts consider CJM one of the essential business process optimization tools, on par with CRM systems.
Why Use a CJM
Did you know that, according to Benchmark data, over 90% of customers conduct their own research online before purchasing your products or services? And most of them find at least a few offers similar to yours?
Why did they choose you – and will they choose you again next time? Will they recommend your brand to their family, friends, and acquaintances?
A well-designed Customer Journey Map can give you a realistic answer to these questions.
The Purpose of a Customer Journey Map: How to Turn Plans Into Real Sales
You’ve analyzed your product’s market niche, defined your target audience, mapped out the ideal customer journey, and even estimated potential sales volumes.
But the actual results fall short of expectations, and potential buyers are abandoning their shopping carts and not becoming repeat customers?
Then it’s the perfect time to start creating Customer Journey Maps.
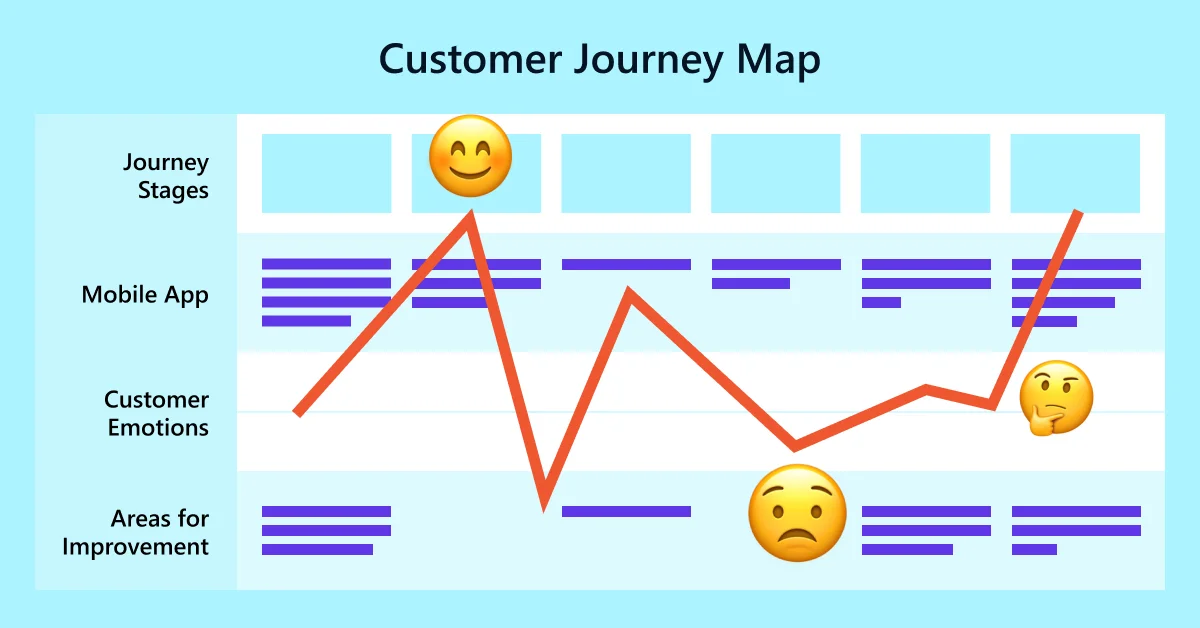
The foundation of CJM is analyzing the interests, needs, motives, and emotions of customers at each stage of interaction with the brand. These maps are usually created as tables, diagrams, or infographics.
This approach helps visualize the pain points along the customer journey – from the first contact with the company to post-sale interactions.
It gives businesses the opportunity to understand how customers perceive a product, service, or solution, to identify growth areas, and to suggest relevant improvements for related business processes.
Building a Customer Journey Map is useful at any stage of business development.
The Benefits of a Detailed Customer Journey Map
The more information you gather when creating a Customer Journey Map, the higher the chances of accurately reflecting the processes specific to your business.
A detailed CJM always offers extra opportunities:
- The more detailed the map, the easier it is to spot real obstacles along the customer path – such as a registration form that freezes, unclear instructions, or an overloaded support line. Stepping beyond the “average journey” allows you to address conversion issues in a targeted way and significantly improve results.
- Detailed CJMs visualize the behavior of different types of real customers, their expectations, and the barriers they face. This enables businesses not only to create highly customized content and personalized offers but also to configure automated scenarios that actually work.
Involve your CRM system in creating a detailed CJM; make full use of web analytics data; analyze support service call records; interview managers and focus groups.
Tip: Don’t overlook customer feedback – according to a Forbes survey conducted in 2023, 50% of respondents are willing to share their data with companies in exchange for better service and a positive customer experience.
Key Elements of a Customer Journey Map
A Customer Journey Map is always created with the specifics of each business and product in mind. However, the core elements are usually universal. These include:
- Journey Stages – a list of all significant interaction points between customers and the company. For example: awareness, exploring offers and comparing competitors, making purchase decisions, buying, service, and post-sale support.
- Touchpoints – specific places or channels through which the customer interacts with the company: website, social media, popular messengers, offline or online stores.
- Customer Emotions at each stage.
Tip: Don’t spare resources or effort to find out how customers feel at every stage of their journey. According to research by one of the most influential American consumer behavior companies, PWC, 32% of consumers say they are ready to abandon their favorite brand after just one negative experience.
- Customer Goals – understanding what the customer wants at each stage: to find information, receive a discount, or solve a problem (what problem, and how).
- Pain Points – obstacles on the customer’s path. These might include inconvenient website navigation, a complicated payment process, poor warranty service, late delivery, or lack of communication about changes to delivery conditions or timing.
When identified in time, these obstacles turn into growth opportunities for the company.
Tip: Focus on building long-term, trust-based relationships with your customers. Do everything you can to make them want to recommend you. According to Benchmark data, 70% of companies report that referral leads convert into sales faster than any other type of lead.
Build Your CJM the Right Way
Creating an effective Customer Journey Map involves following a clear sequence of essential steps.
Defining the Goal
Start by clearly defining your business goal – whether it’s gaining a specific market share, achieving ROI, or increasing profits – and set a pool of relevant, measurable metrics.
For example: Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Retention Rate, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), Conversion Rate, Average Resolution Time, return or complaint rate, and Customer Engagement Metrics.
Map Creation is a Team Effort
It’s important to involve all employees who interact with customers in the CJM creation process – including service staff, after-sales support teams, and salespeople.
This ensures a comprehensive view, effective identification of pain points, and synchronized efforts to implement a customer-centric approach.
A Complete List of Touchpoints
Make sure you capture every single touchpoint where customers interact with your brand at each stage of the journey.
In-Depth Target Audience Analysis
This step is based on:
- Data from the CRM system, including sales analytics and customer support records,
- Web analytics and behavioral insights using tools like Microsoft Clarity,
- Social media analysis and marketing campaign analytics,
- Field research, including surveys and focus groups,
- Customer feedback gathered via support chatbots, reviews on marketplaces, and forum discussions.
Tip. Communicate with your customers via the channels that are convenient for them. According to Benchmark research, businesses that adopt an omnichannel sales strategy reach a customer retention rate of 89%.
Audience Segmentation
It’s essential to break your customer base into separate segments and create detailed personas for each one. The segmentation criteria will depend on your business specifics and objectives. Typically, these include:
- Socio-demographic factors: age, gender, job title, income level, marital status, education,
- Geographic factors: region, area, and local consumption patterns,
- Buying behavior: purchase frequency, timing, and decision drivers (necessity, impulse, etc.),
- Psychographic factors: values and lifestyle.
Testing the Customer Journey Map
Once your CJM is complete, test it by simulating real-life scenarios with focus groups. Afterward, start developing a clear action protocol for each department – based on customer types and journey stages.
Use A/B testing to identify the most effective improvements for different customer segments.
Process Optimization at Pain Points
Identified customer pain points must be transformed into targeted improvements – such as refining website UI/UX, streamlining the order process, or enhancing delivery service operations.
Measuring Core KPIs
It’s crucial to regularly assess the effectiveness of your implemented changes by tracking relevant metrics.
Key Types of Customer Journey Maps
Let’s take a closer look at the most common formats for visualizing customer journeys.
Current State Customer Journey Map
This type of map reflects customer thoughts and feelings throughout their interactions with the company.
It highlights emotions and issues at each touchpoint and is particularly useful for identifying gaps in the customer experience.
Tip: When working to improve customer experience, remember that – according to research by PWC – customers value speed, convenience, helpful staff, and a friendly yet non-intrusive service approach the most.
Day in the Life – Stepping into the Customer’s Shoes
This CJM format models an entire day in the life of a potential customer. It’s a valuable tool for proactive businesses.
For example, future parents might not yet be actively searching for educational programs for their child, but they can already be engaged with interactive early development solutions.
Future State – The Best Way to Model the Ideal Customer Journey
This type of Customer Journey Map focuses on carefully designing every stage of the customer journey – including potential pain points – to envision the perfect experience.
Tip. Don’t hesitate to invest time and effort into answering the question: “What more can I do for my customers?”. According to PWC research, 54% of Americans believe that most companies need to improve their customer experience.
Organize Customer-Centric Business Processes
A Customer Journey Map built on the Service Blueprint approach aims to “audit” the teams and processes involved in customer service. One of the key growth opportunities here is relieving employees of routine tasks, allowing them to focus on customer care and attention.
Tip. According to Benchmark, introducing AI into the sales process can take over up to 40% of routine tasks.
Customer Journey Map Examples for B2C and B2B
Example: Customer Journey Map for a Car Service Center (B2C)
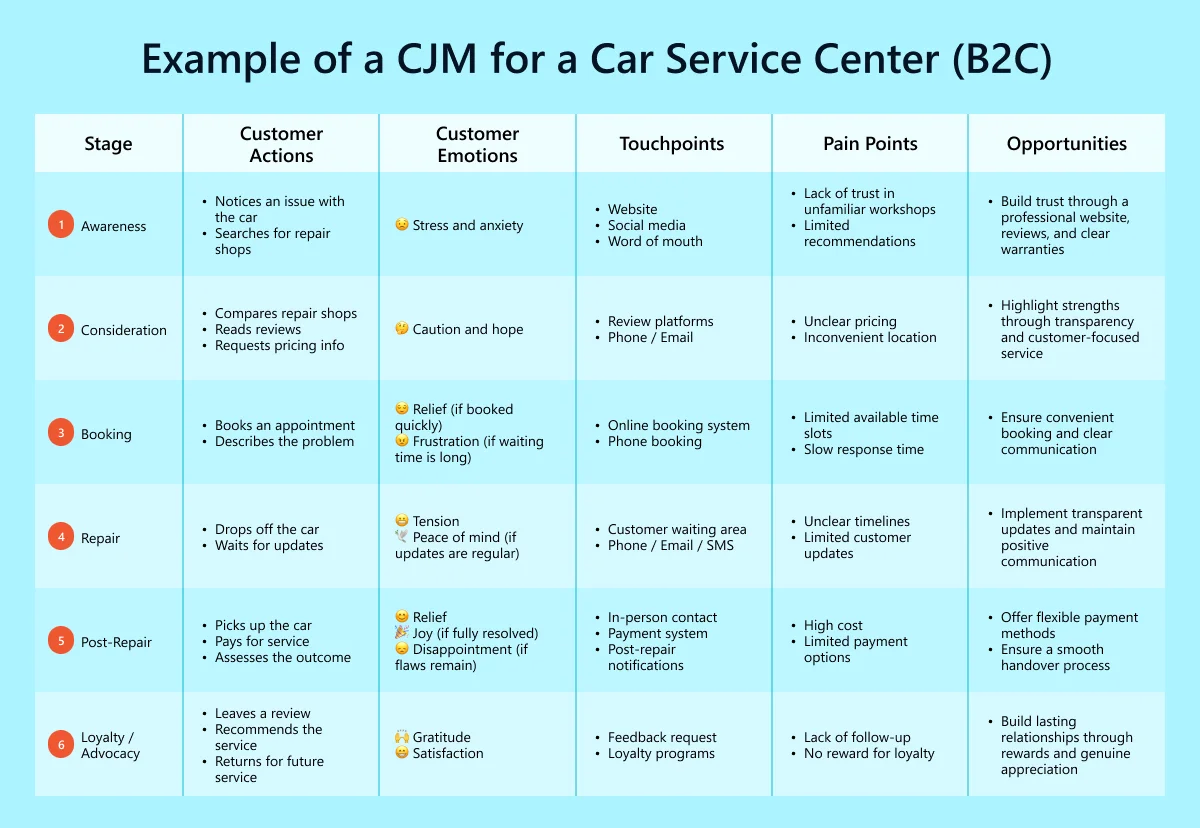
Example of a CJM for a CRM System Provider (B2B)
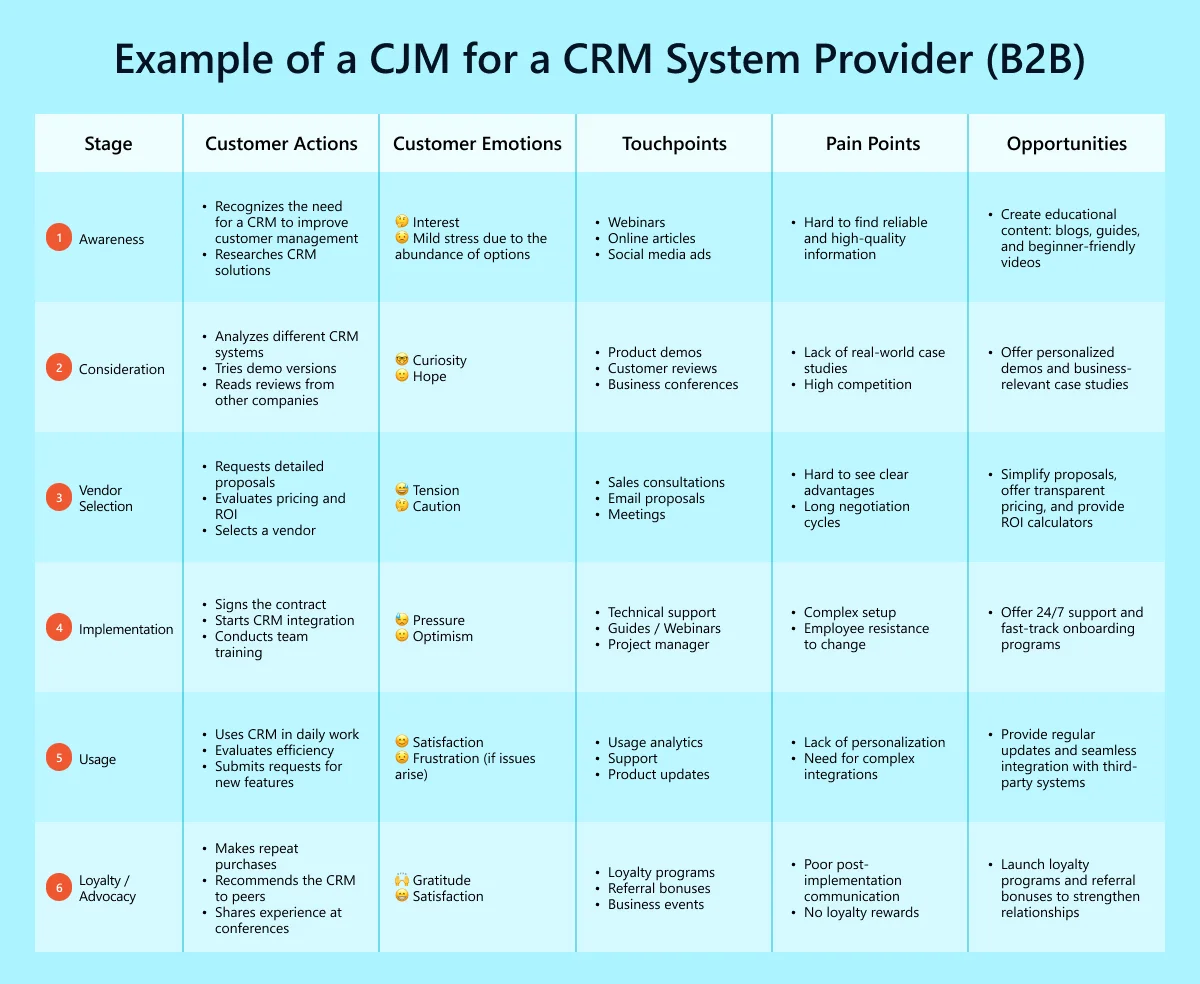
Best Practices for Customer Journey Mapping
- It’s important to clearly define the goal before creating a customer journey map. For example, if a company wants to reduce customer churn and focus on retention, it’s essential to carefully address post-purchase pain points.
- Study real customers, not hypothetical ones, and build the CJM based on data, not assumptions. Draw relevant conclusions from the data you collect. For example, if customers often contact support right after registration, it might be necessary to refine this process.
- Create detailed customer personas. A customer journey map should be built for specific audience segments.
- Carefully analyze the emotional state of customers. You can add a mood scale from negative to positive and highlight critical moments. For example, if new users feel confused, consider adding video tutorials or automated tips.
- Use digital tools to build your CJM.
- Optimize bottlenecks and test improvements. After all, a customer journey map is a tool for driving necessary changes. For example, if customers often abandon their shopping cart, you could test adding a “Buy in one click” option.
10 Common Mistakes in Customer Journey Mapping
- Building a CJM without real data. This risks wasting resources on improving things that are not critical for customers.
- Creating a customer journey map for an “average” client, without clearly defined personas.
- Ignoring the customer’s emotional state.
- An incomplete set of touchpoints.
- No map of the ideal scenario, focusing only on “as-is” without understanding what the “to-be” state should look like.
- Ignoring negative customer experiences and focusing only on positive interactions.
- A map that’s either too detailed or too general. The optimal balance is 5–10 main stages with clearly defined touchpoints.
- No CJM updates: it’s important to regularly analyze changes in customer behavior and update the map at least once every six months.
- Creating a CJM as a formality: this is a decision-making tool meant to drive process changes.
- Lack of cross-functional collaboration: a CJM should not be created solely by the marketing team without involving other specialists.
Tools for Creating a Customer Journey Map
The main requirements for CJM tools are:
- Interactivity and advanced visualization capabilities,
- Integration with CRM systems and other data sources,
- Collaboration features for team workflows,
- Advanced analytics and automation options.
Microsoft Visio
A tool for creating diagrams, charts, and visualizations, including CJM. It offers ready-made blocks and templates for building maps.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights enables the analysis of customer journey based on data from various channels. It also uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze customer behavior.
Microsoft Power BI
A platform for data analytics and visualization that can be used, among other things, for CJM analysis. It allows the creation of custom CJMs based on data from different sources.
Microsoft Whiteboard
An intuitive and simple tool for collaborative teamwork, integrated with Teams and Outlook. Suitable for creating CJMs at the early stages of business development.
In addition to these, there are also a number of specialized tools
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a Customer Journey Map and a User Journey?
A Customer Journey Map is a global view of the customer and their experience. It covers all stages of interaction with the company and includes all channels. It focuses on emotions, pains, expectations, and the overall consumer experience. It is used for strategic customer experience management.
A User Journey, on the other hand, is a specific scenario of user interaction with a product or digital service. It usually covers a single scenario or case. It is used when the goal is to optimize interactions with a website or app and improve UX/UI.
What’s the difference between a Customer Journey Map and a Sales Funnel?
A Customer Journey Map and a sales funnel are two different approaches to analyzing customer interaction. The sales funnel is a model that describes the path of a potential customer from the first contact with the brand to the purchase. It focuses on business outcomes and conversion. It is more oriented toward marketing and sales, rather than the entire customer experience. It helps increase sales effectiveness and the ROI of advertising campaigns.
The funnel helps identify weak points in sales (e.g., high abandonment rate at the checkout stage). A CJM helps understand the reasons behind the problem (e.g., an unclear or inconvenient website interface).
What’s the difference between a Customer Journey Map and a Customer Experience Map?
A Customer Experience Map (CEM) is a broader overview of customer interaction with the company throughout their entire lifecycle, regardless of the specific scenario, compared to a Customer Journey Map.
It focuses on the overall, brand-independent experience. It analyzes all interactions and the consumer context, from when they’re unaware of the company to when they become a loyal customer or leave the brand. It helps identify opportunities for improving the overall customer experience.
How to use a Customer Journey Map?
A CJM is a powerful tool for identifying ways to improve products, building successful marketing strategies, and establishing effective communication with consumers to increase loyalty and attract new customers.
A CJM combined with a CEM allows you to assess customer interactions with the company comprehensively and improve both the overall business strategy and specific processes.
It is also effective to combine a CJM with a sales funnel. The funnel visualizes the problem, while the CJM helps understand how to solve it.
Combining a CJM with a User Journey helps improve customer experience at a strategic level while simultaneously optimizing the company’s digital services.
What SMART business solutions are useful for creating a Customer Journey Map/improving the Customer Journey?
SMART business offers a range of comprehensive solutions for collecting and analyzing the information necessary to optimize business processes and build a CJM. These include: SMART Sales, SMART Customer Care, SMART Order Management and SMART Marketing, with a full suite of extensions for organizing omnichannel communication and 24/7 service support.
Would you like to learn more about how to optimize your business’s IT ecosystem to create a maximally customer-oriented service? Register for a free consultation here.